16 Greenhouse gases warm the planet Scientists know with virtual certainty that increasing greenhouse gas concentrations tend to warm the planet In computerbased models, rising concentrations of greenhouse gases produce an increase in the average surface temperature of the earth over time1019 Although greenhouse gases make up only about 1 percent of the Earth's atmosphere, they regulate our climate by trapping heat and holding it in a kind of warmair blanket that surrounds the planet Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, trap the heat that reflects back from the surface inside Earth's atmosphere

Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
What are the 4 most common greenhouse gases
What are the 4 most common greenhouse gases-The release of greenhouse gases (GHGs) and their increasing concentration in the atmosphere is leading to a changing climate This change has an impact on the environment, human health and the economy This indicator tracks GHG emissions and provides consistent information on emissions from the largest emitting facilities in CanadaGreenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climate change since the mid th century 1 The indicators in this chapter characterize emissions of the major greenhouse gases resulting from human activities, the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere, and how emissions and concentrations have changed over time
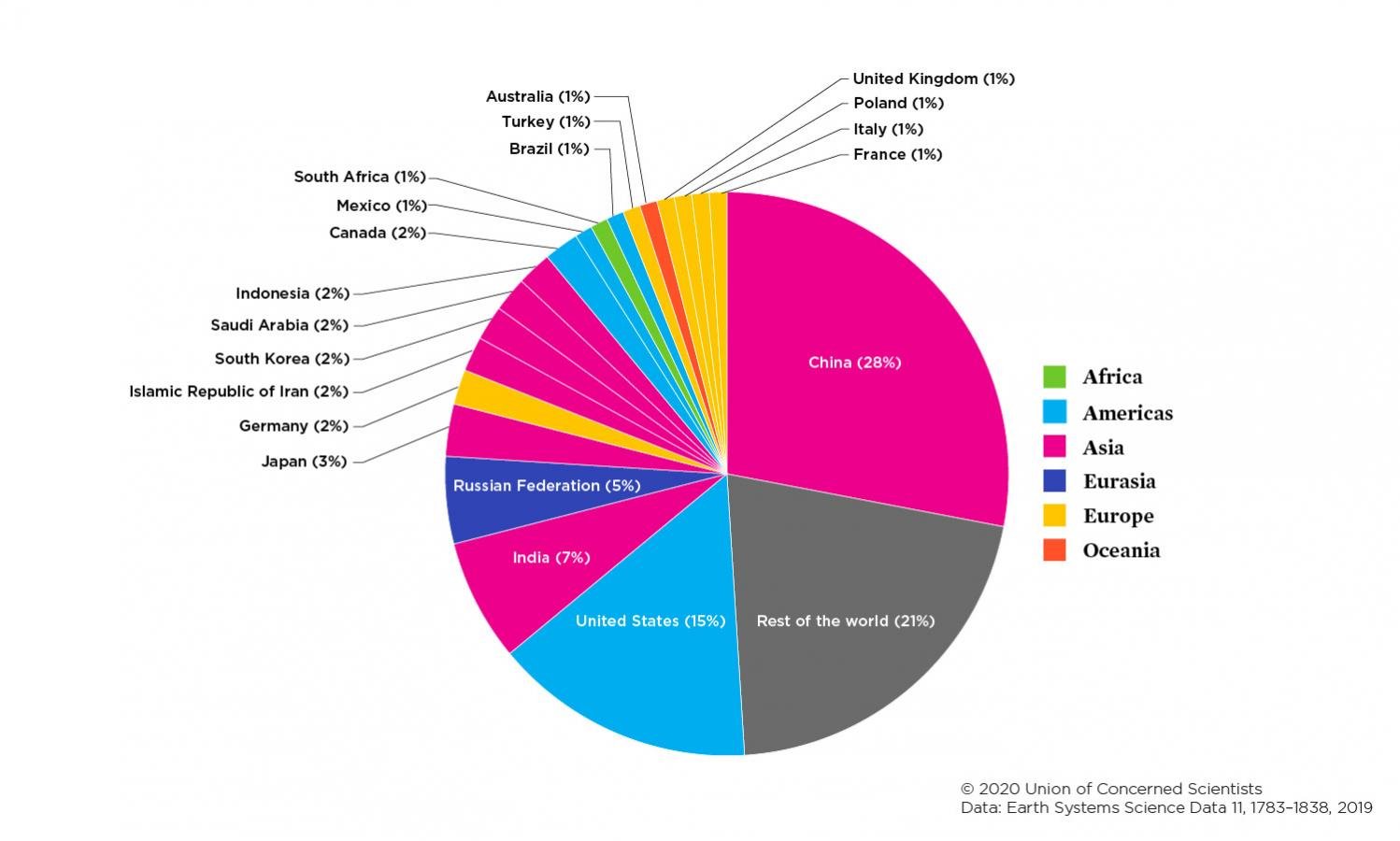



Each Country S Share Of Co2 Emissions Union Of Concerned Scientists
Greenhouse gases are a group of compounds that are able to trap heat (longwave radiation) in the atmosphere, keeping the Earth's surface warmer than it would be if they were not present1 These gases are the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect2 Increases in the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere enhances the greenhouse effect which is creating globalGreenhouse gases absorb this infrared radiation to trap heat in the atmosphere Greenhouse gases can absorb and emit infrared radiation within the thermal infrared range The major greenhouse gases are Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), Water vapour (H 2 O), Methane (CH 4 ), Nitrous oxide (N 2 O), Chlorofluoro carbons and perfluorocarbons (CFCs and PFCs)1 Light Right The best place to start saving and reducing greenhouse gases is by choosing the right lighting options for your living space or office With so many different ways to light your home, here are our top tips Get the right bulb Light bulbs say a
Greenhouse gases contribute towards the greenhouse effect Before industrialization and the rapid rise in the world's population, this was always at a manageable level, allowing the effect to warm the earth in a balanced, natural way But with industrialization, greenhouse gasses Greenhouse gases include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane, nitrous oxide, halogenated fluorocarbons, ozone, perfluorinated carbons, and hydro fluorocarbons These gases surround and insulate the Earth like a blanket They allow the sun to reach and warm the Earth's surface then block the warmth from escaping back into spaceThe greenhouse effect is caused by the interaction of the sun's energy with greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and fluorinated gases in the Earth's atmosphere
The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directionsPart of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming itGlobal warming The greenhouse effect is essential for the sustainability of life on earth Had it not been for greenhouse gases, the average temperature of the earth would have been 18℃ in comparison to normal levels, which is 15℃WHAT IS THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of life Human action, however, has increased the presence of these gases




Greenhouse Gases Climate Change By Sarah Duffer




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
To stop climate change, we need to stop the amount of greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, from increasingFor the past 150 years, burning fossil fuels and cutting down forests, which naturally pull carbon dioxide out of the air, has caused greenhouse gas levels to increase There are two main ways to stop the amount of greenhouse gases from increasing we can stopGreenhouse gases include water vapor, CO2, methane, nitrous oxide (N2O) and other gases Carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases turnThe study report on the Greenhouse gases and their impact on Global warming Without the greenhouse effect the Earth's average global temperature would be much colder and life on Earth as we know it would be impossible Greenhouse gases include water vapor, CO2, methane, nitrous oxide (N2O) and other gases




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
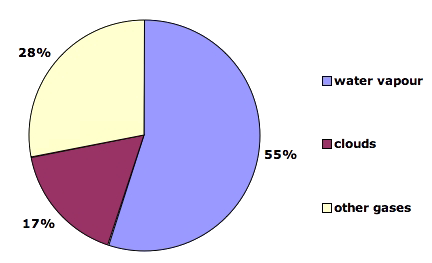



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici
Explore this interactive graph Click and drag to display different parts of the graphTo squeeze or stretch the graph in either direction, hold your Shift key down, then click and drag This graph (source data) shows the combined warming influence of longlived greenhouse gases as a fraction of their 1990 influenceAmplifying the greenhouse effect Although carbon dioxide is often considered the worst greenhouse gas, it is not actually true However, since there is more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere than any other greenhouse gases emitted by humans (only topped by water vapor), it does have the most obvious impact 3 Methane Methane is the next on our top 5 list of greenhouse gasesGreenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclear French mathematician Joseph



Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Transport In Europe European Environment Agency




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament
Greenhouse gases and their harmful effects Greenhouse gases are substances that contribute to the greenhouse effect The most significant gases contributing to climate change are water vapour (H 2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), ozone and dinitrogen oxide (N2O), which are also naturally present in natureEvaluating their Significance Environmental Impact Assessment Guide to Acknowledgements Working Group This practitioner's guide has been developed and mitigation for an assessment of greenhouse gas emissions Finally, section 7 looks at how best to communicate the assessment within an Environmental Texas, Leader in Greenhouse Gases, Stands Vulnerable to Their Effects The Fayette coal plant outside Austin State officials have argued that reducing emissions would drive up electricity prices




Greenhouse Gases Bioninja



The Greenhouse Effect
The most abundant greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, and chlorofluorocarbons Additionally, atmospheric water vapor also contributes to the occurrence of the greenhouse effectRice cultivation has contributed considerably to increased greenhouse gases; The gasses which are responsible for causing global warming are called 'greenhouse gasses' The harmful effects of presence of greenhouse gasses in atmosphere are global warming, climate change, ozone depletion, sea level rise, adverse effects on biodiversity etc
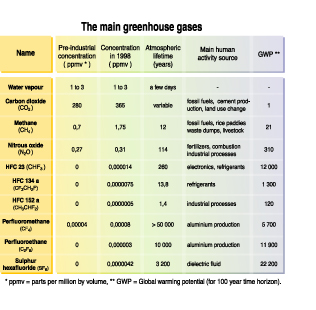



Main Greenhouse Gases Grid Arendal
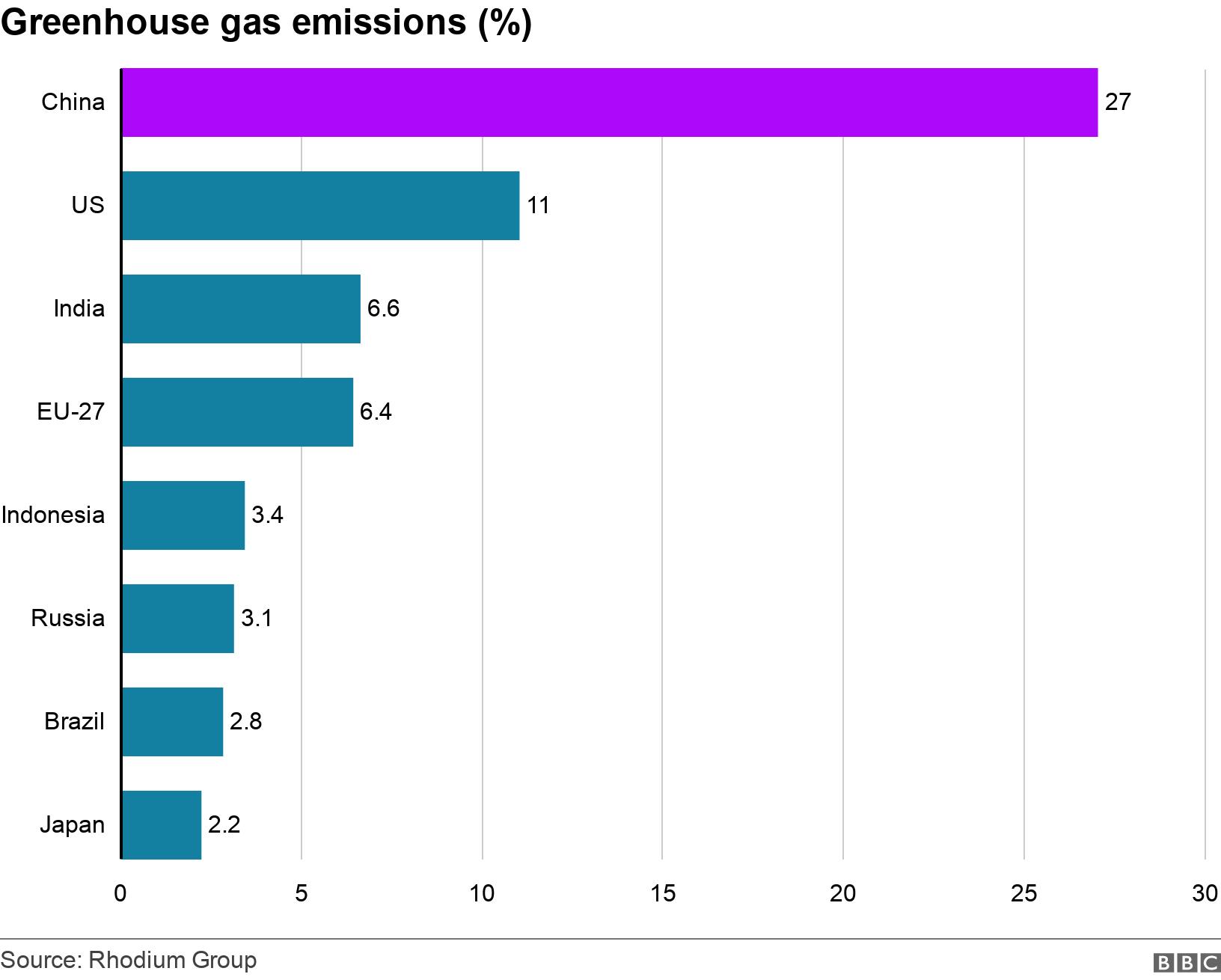



Report China Emissions Exceed All Developed Nations Combined c News



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿